New York
- Address:2972 Westheimer Rd. Santa &, Illinois 85486
- Phone:+8801761456456
- Email:[email protected]

BMI Vs Body Composition: Which Is Better BMI Or Body Composition?
BMI Vs Body Composition: Which Is Better BMI Or Body Composition?
If you’ve ever wondered about the best way to measure your body’s health and fitness, you’ve likely come across the terms “BMI” and “body composition.” But which one is better? Is it BMI, the traditional method based on height and weight, or body composition, which takes into account factors like muscle mass and body fat percentage? In this article, we’ll dive into the debate of BMI vs body composition and help you understand the pros and cons of each.
When it comes to assessing our bodies, we often rely on the trusty BMI, or Body Mass Index. It’s a quick and easy calculation that provides an estimate of our body fatness based on our height and weight. But is it really the best measure of our overall health and fitness? On the other hand, body composition analysis takes a more detailed approach, considering factors such as muscle mass, body fat percentage, and even bone density. It provides a more comprehensive understanding of our body’s composition and can give us a clearer picture of our overall health. So, which one should you choose? Let’s delve deeper into the world of BMI vs body composition and find out which method reigns supreme.
BMI (Body Mass Index) and body composition are two different ways to assess a person’s physical health and fitness. While BMI provides a general idea of whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese based on their height and weight, body composition provides a more detailed analysis of the distribution of fat, muscle, and bone in the body.
Although BMI is widely used and easy to calculate, it has limitations as it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or body shape. On the other hand, body composition analysis provides a more accurate assessment of overall health and can help identify specific areas for improvement.
In conclusion, while BMI can be a useful tool for initial screening, body composition analysis offers a more comprehensive picture of an individual’s health and fitness levels. Therefore, it is generally considered better to focus on body composition rather than relying solely on BMI.
BMI vs Body Composition: Which is Better?
When it comes to assessing our overall health and fitness, two commonly used methods are BMI (Body Mass Index) and body composition analysis. Both provide valuable insights into our body composition and can help us understand our health status. However, they differ in their approach and the information they provide. In this article, we will explore the differences between BMI and body composition analysis and determine which method is better for assessing our health and fitness.
What is BMI?
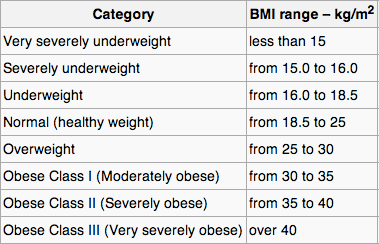
BMI is a widely used measurement that calculates an individual’s body fat based on their height and weight. It is a simple calculation that divides a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. The resulting number indicates whether the person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese, based on predefined ranges.
While BMI is a convenient tool for quick assessments, it has limitations. It does not take into account factors such as muscle mass, bone density, or distribution of fat, which can vary greatly among individuals. As a result, BMI may not accurately reflect an individual’s overall health and body composition.
The Limitations of BMI
One of the main limitations of BMI is that it does not differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass. This means that individuals with a higher muscle mass, such as athletes or bodybuilders, may be classified as overweight or obese, even though they have a low percentage of body fat. On the other hand, individuals with a low muscle mass and a higher percentage of body fat may fall within the normal weight range, despite having an unhealthy level of body fat.
Additionally, BMI does not take into account the distribution of fat in the body. Accumulation of fat around the waist, known as visceral fat, is associated with a higher risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. However, BMI does not provide any information about the distribution of fat, making it less effective in assessing an individual’s risk for these diseases.
What is Body Composition Analysis?
Body composition analysis is a more comprehensive method of assessing an individual’s body composition. It provides a detailed breakdown of the different components that make up our bodies, including fat mass, muscle mass, bone density, and water content. This analysis can be done using various techniques such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), or skinfold measurements.
By analyzing these components, body composition analysis can provide a more accurate assessment of an individual’s overall health and fitness. It can help identify imbalances in body composition, such as excessive fat mass or low muscle mass, which may indicate a higher risk of chronic diseases or poor physical performance.
The Benefits of Body Composition Analysis
One of the main advantages of body composition analysis is its ability to differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass. This means that individuals with a higher muscle mass will not be classified as overweight or obese solely based on their weight and height. Instead, their body composition analysis will provide a more accurate representation of their overall health and fitness.
Furthermore, body composition analysis can provide valuable information about the distribution of fat in the body. This is particularly important as the accumulation of visceral fat around the waist is associated with a higher risk of chronic diseases. By assessing the distribution of fat, body composition analysis can help identify individuals who may be at a higher risk and guide them towards appropriate interventions to reduce their risk.
BMI vs Body Composition: Which is Better?
While BMI is a convenient tool for quick assessments, it has limitations when it comes to accurately assessing an individual’s overall health and body composition. On the other hand, body composition analysis provides a more comprehensive and accurate assessment by analyzing different components of the body.
For individuals who fall within the normal BMI range, body composition analysis can provide valuable insights into their muscle mass, fat mass, and distribution of fat. This information can help guide them towards making appropriate lifestyle changes to improve their overall health and fitness.
The Importance of Individualized Assessments
It’s important to note that both BMI and body composition analysis have their place in assessing health and fitness. However, it is crucial to understand their limitations and consider individual circumstances when interpreting the results. For a more accurate assessment, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or fitness expert who can provide personalized insights based on a combination of BMI, body composition analysis, and other relevant factors.
In conclusion, while BMI can provide a quick assessment of weight status, body composition analysis offers a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s overall health and fitness. By considering factors such as muscle mass, fat mass, and the distribution of fat, body composition analysis can provide valuable insights that go beyond what BMI alone can offer.
Key Takeaways: BMI vs Body Composition
- BMI is a simple calculation based on height and weight, while body composition refers to the proportion of fat, muscle, and other tissues in the body.
- BMI can give a general idea of whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese, but it doesn’t provide information about body fat percentage or muscle mass.
- Body composition analysis provides a more accurate assessment of overall health and fitness by measuring body fat percentage, muscle mass, and other factors.
- BMI is widely used in healthcare and research due to its simplicity, but body composition analysis is becoming increasingly popular for personalized health and fitness goals.
- When it comes to determining overall health and fitness, body composition analysis is considered better than BMI as it provides a more comprehensive understanding of the body’s composition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What is the difference between BMI and body composition?
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a simple calculation that uses a person’s height and weight to determine their level of body fat. It is a widely used tool to categorize individuals into different weight categories, such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. On the other hand, body composition refers to the proportion of fat, muscle, bone, and water in the body. It provides a more detailed analysis of a person’s body composition beyond just their weight and height.
While BMI only takes into account weight and height, body composition analysis considers factors such as muscle mass, body fat percentage, and distribution of fat throughout the body. This allows for a more accurate assessment of an individual’s overall health and fitness level.
Question 2: Is BMI or body composition a better indicator of overall health?
Both BMI and body composition can provide useful information about a person’s health, but they focus on different aspects. BMI is a quick and easy method to assess weight status and identify potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese. It is often used as a screening tool in population studies.
On the other hand, body composition analysis provides a more detailed understanding of an individual’s body composition, including the proportion of fat and muscle. This information can be valuable in determining overall health and fitness level, as excess body fat and low muscle mass have been linked to various health conditions.
Question 3: Can BMI be inaccurate for certain individuals?
Yes, BMI can be inaccurate for certain individuals. While it is a useful tool for assessing weight status in the general population, it may not accurately reflect body fat levels in certain individuals, such as athletes or individuals with higher muscle mass. This is because muscle weighs more than fat, and BMI does not take into account the difference in composition.
Additionally, BMI does not consider the distribution of fat in the body. Two individuals with the same BMI may have different body compositions, with one having more visceral fat (fat around organs) which is associated with a higher risk of health problems. Therefore, it’s important to consider other factors, such as body composition analysis, for a more accurate assessment of health.
Question 4: How can body composition analysis be measured?
Body composition analysis can be measured using various methods, including dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), skinfold thickness measurements, and air displacement plethysmography. Each method has its own advantages and limitations.
DXA is considered one of the most accurate methods as it measures bone mineral density, fat mass, and lean mass. BIA is a commonly used method that measures electrical impedance to estimate body composition. Skinfold thickness measurements involve pinching the skin in specific areas to measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat. Air displacement plethysmography measures body volume by calculating the amount of air displaced within a closed chamber.
Question 5: Which is more important, BMI or body composition?
Both BMI and body composition provide valuable information about a person’s health, but their importance may vary depending on individual circumstances. BMI is a useful screening tool to assess weight status and identify potential health risks associated with weight extremes. It is quick and easy to calculate, making it widely used in population studies and clinical settings.
On the other hand, body composition analysis offers a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s overall health and fitness level. It takes into account factors such as muscle mass, body fat percentage, and fat distribution, providing a more accurate assessment of body composition and potential health risks associated with excess body fat or low muscle mass. Therefore, both BMI and body composition can be important, but the specific context and goals of the assessment should be considered.
BMI vs Body Fat
Conclusion: So, which is better: BMI or body composition?
In the battle between BMI and body composition, it’s clear that both have their strengths and weaknesses. While BMI is a quick and easy way to assess overall weight status, it falls short when it comes to providing a complete picture of an individual’s health. On the other hand, body composition analysis offers a more detailed understanding of body fat percentage, muscle mass, and overall fitness level.
However, it’s important to note that neither BMI nor body composition is a perfect measure of health. Both methods have their limitations and should be used in conjunction with other health indicators. The key is to consider multiple factors such as physical activity level, diet, and overall well-being when assessing one’s health status.
Ultimately, the choice between BMI and body composition depends on individual needs and goals. If you’re just looking for a general idea of your weight status, BMI can provide a quick assessment. But if you’re aiming for a more comprehensive understanding of your body composition and overall health, body composition analysis is the way to go. Remember, the numbers on the scale or the BMI chart don’t define your worth or determine your health. What matters most is taking care of your body, nourishing it with nutritious food, staying active, and prioritizing your well-being. So, embrace your unique journey and focus on building a healthy and happy lifestyle that works for you.
Author
Andrea Klas
Andrea Klas, is founder of Andrea Klas Fitness and Andrea Klas Whole Body Fitness. With over 25 years of experience as a successful competitive athlete, and 15 yrs as a Personal Trainer, and Nutrition coach Andrea knows what it takes to be fit, lean and healthy. She has revolutionised the fitness industry with her steadfast commitment to focusing on fat loss, not weight loss and has helped 100’s of women in peri-menopause and menopause lose fat and gain muscle. Compassionate and caring Andrea is committed to helping every client be fit and healthy. Andrea is an entrepreneur, mentor, trusted advisor, speaker, athlete, and mom of 3 boys and lives by her philosophy : EAT real food, LIFT weights, LOVE yourself enough to invest in your health and LIVE your best life.